We typically measure and categorize the entire spectrum of electromagnetic radiation by wavelength and power, with high-energy gamma rays on one end (short wavelengths), and low-energy microwaves and radio waves on the other end (long wavelength). There is a very small range in the middle of the spectrum that is visible to the human eye. Most radiation is invisible to us, such as microwaves and X-rays.
This visible light range is the wavelengths from about 380 nanometers (nm) to 830 nm, bounded by ultraviolet (UV) at the low end of the range and infrared (IR) at the high end.
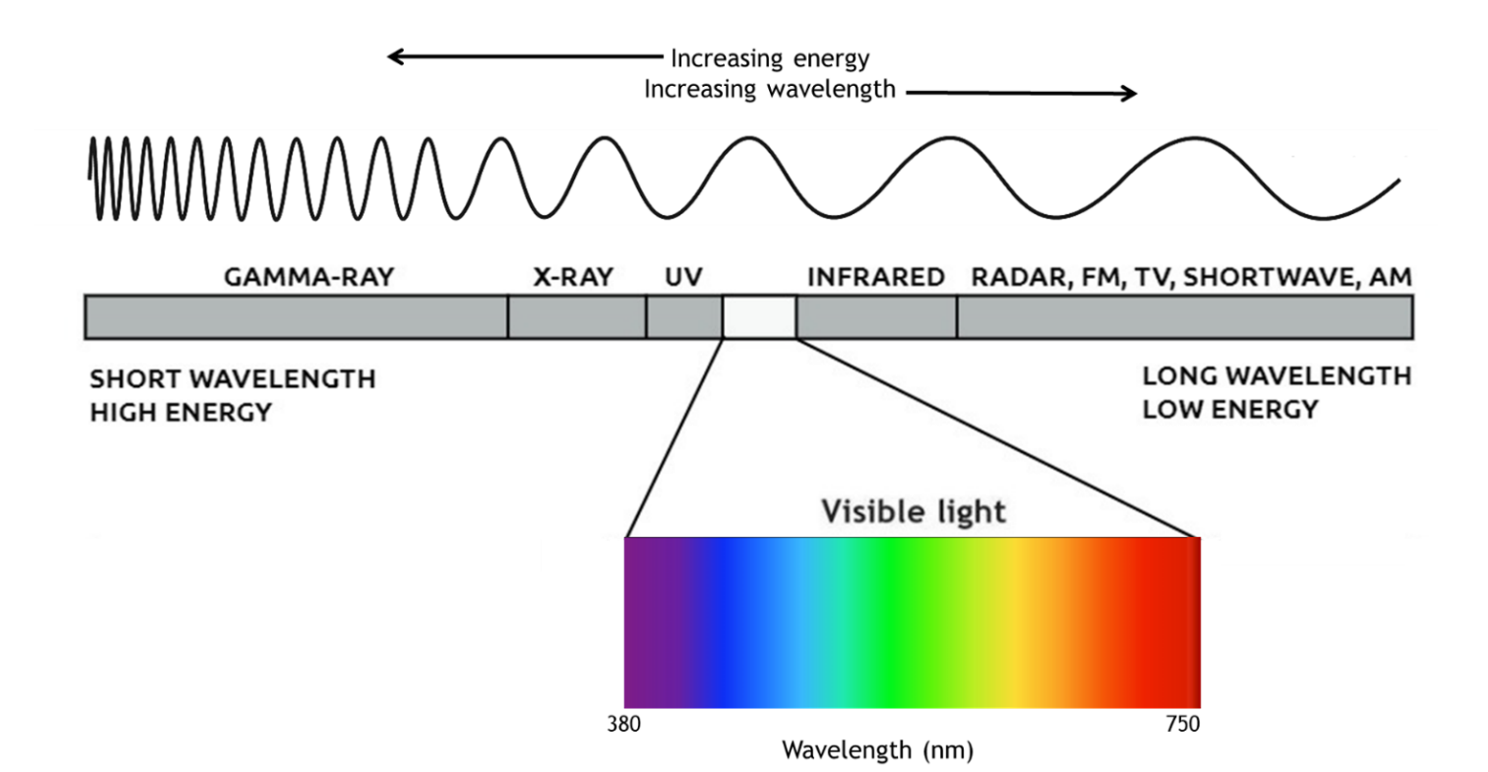
The full spectrum of electromagnetic radiation in the universe, including invisible wavelengths such as X-rays, microwaves, and radio waves. The bottom bar is an expanded view of visible light: the narrow range of the electromagnetic spectrum that the human eye can perceive.
Electromagnetic radiation displays wave-particle duality and it is sometimes more convenient to characterize using the concepts of photon flux and photon energy. An LED example is found in horticulture lighting where the photon flux (measured in μmol/s) is directly related to the photosynthesis rate.
Photon energy is not commonly used in LED technical discussions (everybody is calibrated in nanometers), but the underlying concept that shorter wavelengths have higher photon energy helps in the interpretation of the wavelength sensitivity of a variety of photochemical and photobiological processes.
Radiometric Measurement
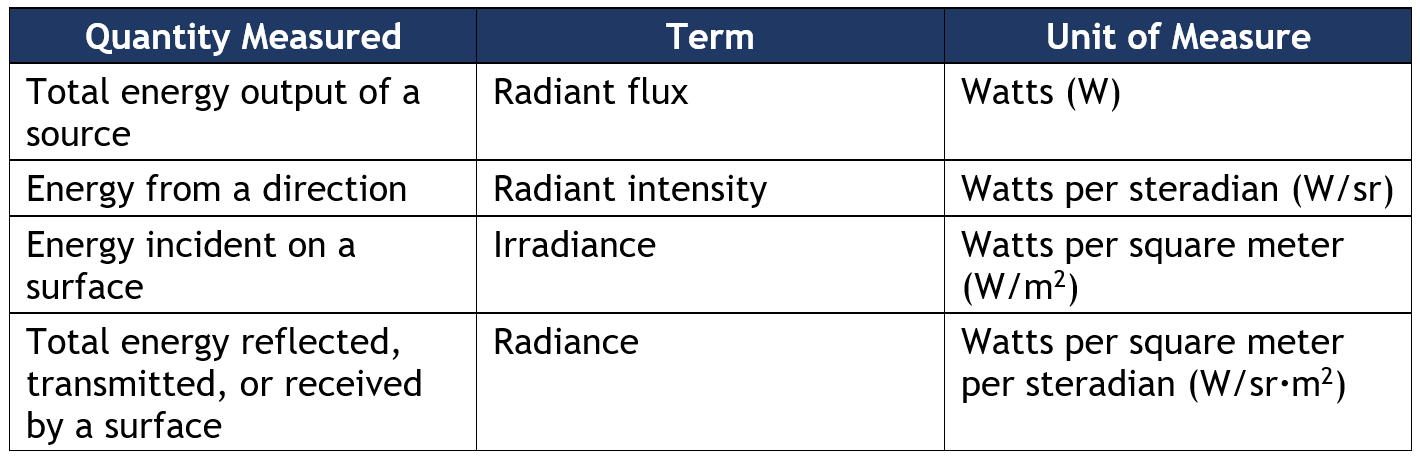
Just as terms like luminance are used to characterize visible light, there is a set of standard measurements that are used to characterize the properties of radiant energy. Measuring all light energy is called radiometry; measuring visible light combined with eye response is called photometry. Radiometry terms and their meanings are:
Radiant flux – measures the total amount of electromagnetic energy emitted by a source, in all directions. Measured in units of Watts (W), named for scientist James Watt. Radiant flux is sometimes also called radiant power.
Radiant intensity – the total amount of energy emitted by a source within a three-dimensional angle. Radiant intensity is measured as the number of Watts per steradian (a unit of solid angular measurement -if a sphere was carved into cones, steradians would be the units of the surface area of each cone where it intersects the outside edge of the sphere).
Irradiance – a measure of the energy that lands on a surface, such as the amount of radiation energy from the sun that lands on a flat area of pavement. Irradiance is measured as Watts per square meter (W/m2).
Radiance – refers to the total energy that is reflected, transmitted, or received by a surface, per angle per area. This is a directional quantity, measured as Watts per steradian per square meter (W/sr·m2)
Radiance is sometimes referred to casually as “intensity” (just as luminance is commonly referred to as “brightness.”). But for technical and scientific purposes, here is a summary of the correct terminology:
Related Luminus Help Center Articles:
What’s the Difference: Luminance, Luminous Flux, Illuminance, Luminous Intensity, Lux, Lumens?
Optical – How do I calculate lux from an LED datasheet?
What do CCT, CIE, and SPD mean in LED lighting?
What is the Color Rendering Index (CRI)?
What’s the difference between color terminology like Hue, Value, and Saturation (Chroma)?
What are the TM-30-18 Color Rendition Guidelines & Reports?
What is the CIE Color Space? What’s the difference between CIE 1931 and CIE 1976?
Useful References:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Luminus Website https://www.luminus.com/
Luminus Product Information (datasheets): https://www.luminus.com/products
Luminus Design Support (ray files, calculators, ecosystem items: [power supplies, lenses, heatsinks]): https://www.luminus.com/resources
Luminus Product Information sorted by Applications: https://www.luminus.com/applications
Where to buy Samples of Luminus LEDs: https://www.luminus.com/contact/wheretobuy.
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Technical Support Contact Information: techsupport@luminus.com
Sales Support Contact Information: sales@luminus.com
Customer Service Support Contact Information: cs@luminus.com

Comments
0 comments
Please sign in to leave a comment.