The Color Quality Scale (CQS) is one method for characterizing the color rendition characters of light sources, particularly solid-state lighting [1]. An early method of characterizing light sources was the Color Rendering Index (CRI). However, it was developed before LED and solid-state lighting became common.
The CRI was based on measurement of light source performance in rendering eight core sample colors using earlier light technologies such as incandescent and fluorescent. While useful for some applications, there are many criticisms of CRI and its usefulness for various color rendering application. Many consider the eight CRI reference color samples to be limited, inaccurate, and too pastel to represent the vividness of the real world. Additionally, with only the core 8 samples considered for CRI scoring, under sampling can lead to inaccuracy.
The Color Quality Scale (CQS) For Solid-State Lighting
To address these concerns, an alternative to CRI is the Color Quality Scale (CQS), developed by the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) in 2010. The CQS is intended to provide more accurate measurement of the color rendering capabilities of solid-state lighting sources and their fidelity (accuracy).
“Instead of only eight unsaturated, pastel colors, the CQS evaluates 15 colors that more accurately span the range of normal object colors across an expanded gamut. In addition, it considers factors including color discrimination and human preference.” [2]
The CQI samples are considered “high chroma,” meaning they have a high saturation of their hue (sometimes also characterized as high purity or high intensity), as shown below. CQS values are calculated on a scale of 0-100, making them easily understood alongside the CRI.
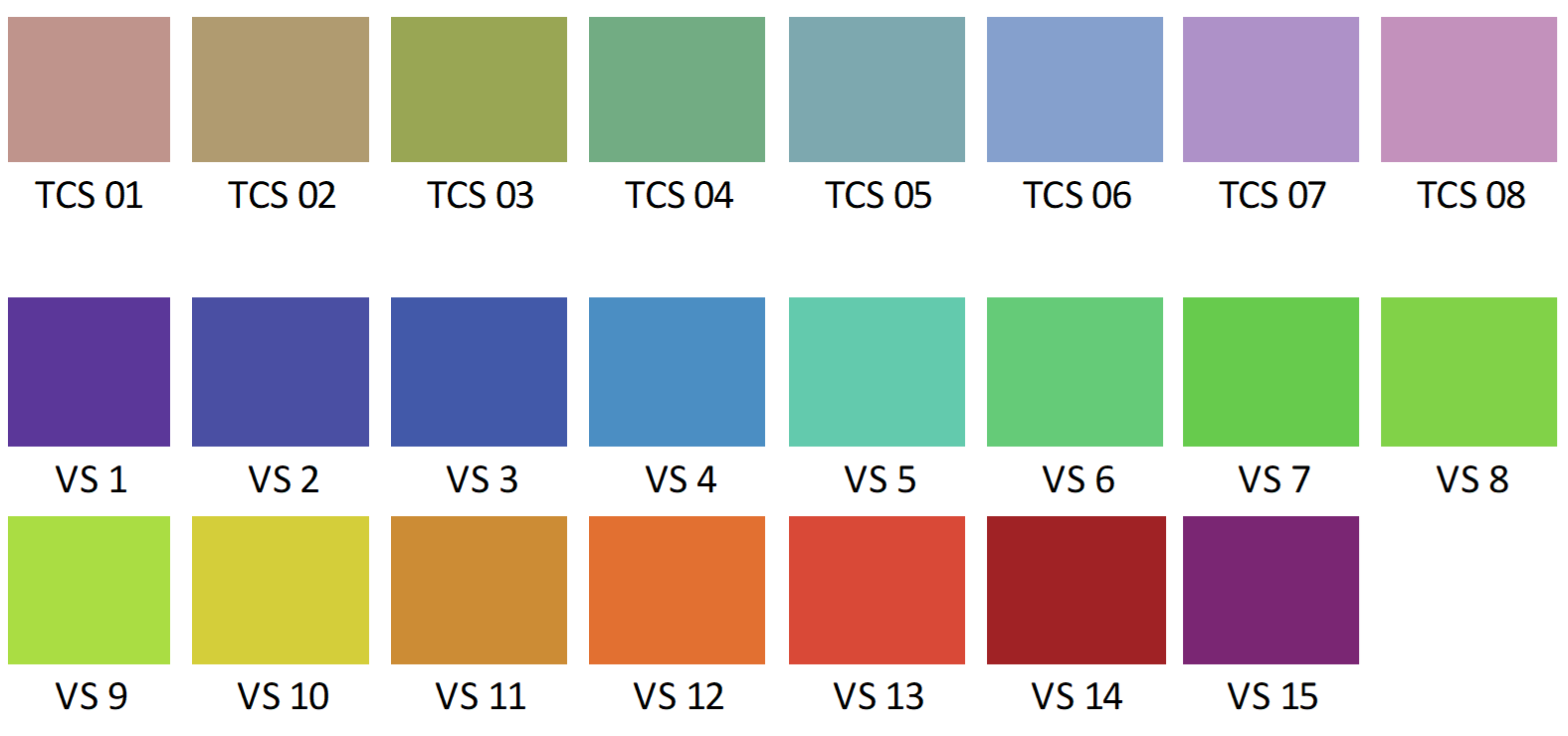
The core CRI color samples (top row) compared to the more saturated 15 CQS color samples (second and third rows) based on the Munsell color system (a three-dimensional representation of color by hue, chroma, and value).
NOTES & REFERENCES
1. Solid-state lighting (SSL) refers to any lighting source that uses semiconductor diodes generate illumination. In contrast to light sources that use electrical filaments (such as or gas (such as fluorescent), SSL lighting types include LEDs (light emitting diodes), OLEDs (organic LEDs), or polymer LEDs.
2. Davis, Wendy & Ohno, Yoshi. (2010). “Color Quality Scale.” Optical Engineering 49(3) March
2010. DOI 10.1117/1.3360335
To learn more, refer to the Help Center articles:
FAQ -> Color Quality Metrics
White Papers -> Achieving Optimal Color Rendition with LEDs
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Luminus Website https://www.luminus.com/
Luminus Product Information (datasheets): https://www.luminus.com/products
Luminus Design Support (ray files, calculators, ecosystem items: [power supplies, lenses, heatsinks]): https://www.luminus.com/resources
Luminus Product Information sorted by Applications: https://www.luminus.com/applications
Where to buy Samples of Luminus LEDs: https://www.luminus.com/contact/wheretobuy.
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Technical Support Contact Information: techsupport@luminus.com
Sales Support Contact Information: sales@luminus.com
Customer Service Support Contact Information: cs@luminus.com

Comments
0 comments
Please sign in to leave a comment.